What is a Gating System?
The gating systems, in the context of casting, is essentially the blueprint required to achieve a smooth and uninterrupted filling of a casting mold cavity.
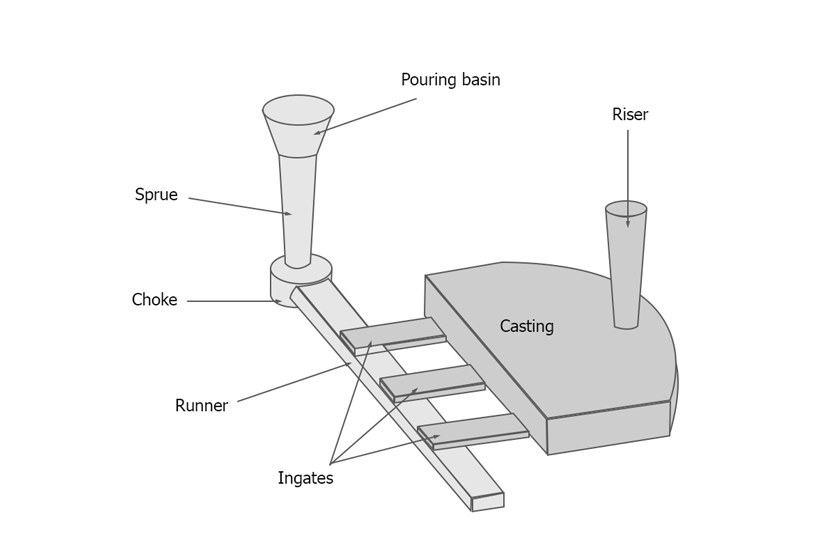
Its purpose is to ensure that molten metal flows cleanly from a ladle into the casting cavity, thus guaranteeing a seamless and proper filling process.
The effectiveness of the gating system hinges on various factors, including the layout of gating channels, such as the positioning and direction of the runner, sprue, and ingates.
Objectives of the Gating System:
A well-designed gating system serves four crucial objectives:
- Clean Molten Metal: The gating system should facilitate the delivery of clean molten metal to the mold cavity, preventing the intrusion of slag and impurities, which can lead to surface imperfections.
- Smooth Filling: A smoothly flowing metal stream reduces turbulence within the mold, contributing to a more stable casting process.
- Uniform Filling: Uniform filling means that the mold cavity is filled in a controlled and even manner, ensuring consistent quality throughout the casting.
- Complete Filling: Complete filling implies that the metal fills the entire cavity with minimal resistance, especially at the end sections, producing thinner sections of metal.
Key Components of a Gating System:
A typical gating system comprises several essential elements:
- Pouring Basin or Bush: This circular or rectangular receptacle collects molten metal poured from the ladle.
- Sprue or Downspout: A circular cross-section channel that directs the molten metal from the pouring basin to the sprue well.
- Sprue Well: This component changes the flow direction of the molten metal at a right angle and guides it into the runner.
- Runner: Responsible for transporting the molten metal from the sprue to the casting.
- Ingate: The final stage of the journey, where the molten metal transitions from the runner into the mold cavity.
- Ladle: The vessel from which molten metal is poured into the gating system.
- Slag Trap or Filter: Positioned within the runner, this component filters out slag as the molten metal flows from the runner to the ingate.
Types of Gating Systems:
The type of gating system employed is influenced by the orientation of the parting plane, which includes the sprue, runner, and ingate.
The primary gating system types are as follows:
- Horizontal Gating System: Widely used, particularly in ferrous metals’ sand casting and gravity die-casting of non-ferrous metals. It’s suitable for flat castings that are filled under gravity.
- Vertical Gating System: Applied in tall castings, typically in high-pressure sand mold, shell mold, and die-casting processes.
- Top Gating System: Utilized when hot metal is poured from the top of the casting. It promotes directional solidification from top to bottom and is well-suited for flat castings to limit initial metal damage.
- Bottom Gating System: Deployed in tall castings where molten metal enters the casting from the bottom.
- Middle Gating System: Combines characteristics of both top and bottom gating systems.
In summary, a well-designed gating system is vital for the success of a casting process.
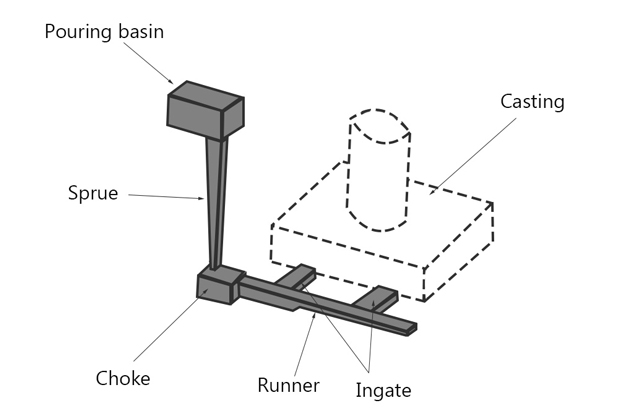
It ensures that clean molten metal flows smoothly, uniformly, and completely into the mold cavity, producing high-quality castings with minimal defects.
The choice of gating system type depends on factors like casting geometry and material, ensuring the optimal outcome for each unique casting project.
Benefits of a Well-Designed Gating System:
A well-structured gating system offers numerous advantages in the casting process, influencing the final quality and efficiency of the castings produced.
Here are some additional insights into the benefits of a meticulously designed gating system:
- Reduced Casting Defects: One of the primary benefits of a proficient gating system is the reduction in casting defects. Proper gating design minimizes the chances of common issues such as shrinkage, porosity, and misruns. This leads to castings with improved structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
- Enhanced Casting Yield: Efficient gating systems maximize casting yield by ensuring that molten metal fills the mold cavity completely and uniformly. This reduces the amount of wasted material, which is especially crucial when dealing with expensive alloys.
- Improved Metallurgical Properties: The gating system has a significant impact on the metallurgical properties of the final casting. An optimized design promotes controlled solidification, reducing the likelihood of microstructural irregularities that can weaken the casting.
- Cost Savings: A well-planned gating system can lead to cost savings by minimizing the need for post-casting operations such as welding, grinding, or machining to rectify defects. This not only saves time but also reduces material wastage.
- Faster Production: Proper gating design can result in quicker filling times, optimizing the overall production cycle. Faster fill times can lead to higher throughput and shorter lead times for casting projects.
- Environmental Benefits: Casting processes that utilize efficient gating systems tend to generate less scrap and waste material. This aligns with sustainability goals and reduces the environmental impact of casting operations.
- Consistency Across Castings: A well-established gating system ensures consistent casting quality across multiple parts or batches. This uniformity is crucial in industries where precision and reliability are paramount.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Experienced foundries often customize gating systems based on the specific requirements of a casting project. This flexibility allows for adaptations to suit different alloys, casting sizes, and geometries.
- Reduction in Post-Casting Work: With an effective gating system, the need for extensive post-casting work, such as removing surface defects or repairing incomplete castings, is significantly diminished. This streamlines the production process and minimizes labor costs.
- Enhanced Control: Gating systems provide a level of control over the casting process, allowing foundries to fine-tune parameters for optimal results. This control extends to factors like pouring temperature, alloy choice, and cooling rates.
In conclusion, a well-designed gating system is more than just a technical necessity; it’s a cornerstone of successful casting operations.
By meeting the objectives of clean, smooth, uniform, and complete metal filling, such systems contribute to high-quality castings, efficient production, cost savings, and environmental responsibility.
Foundries that prioritize gating system design are better positioned to meet the demands of diverse casting projects while maintaining consistently excellent results.

 By Coco
By Coco


